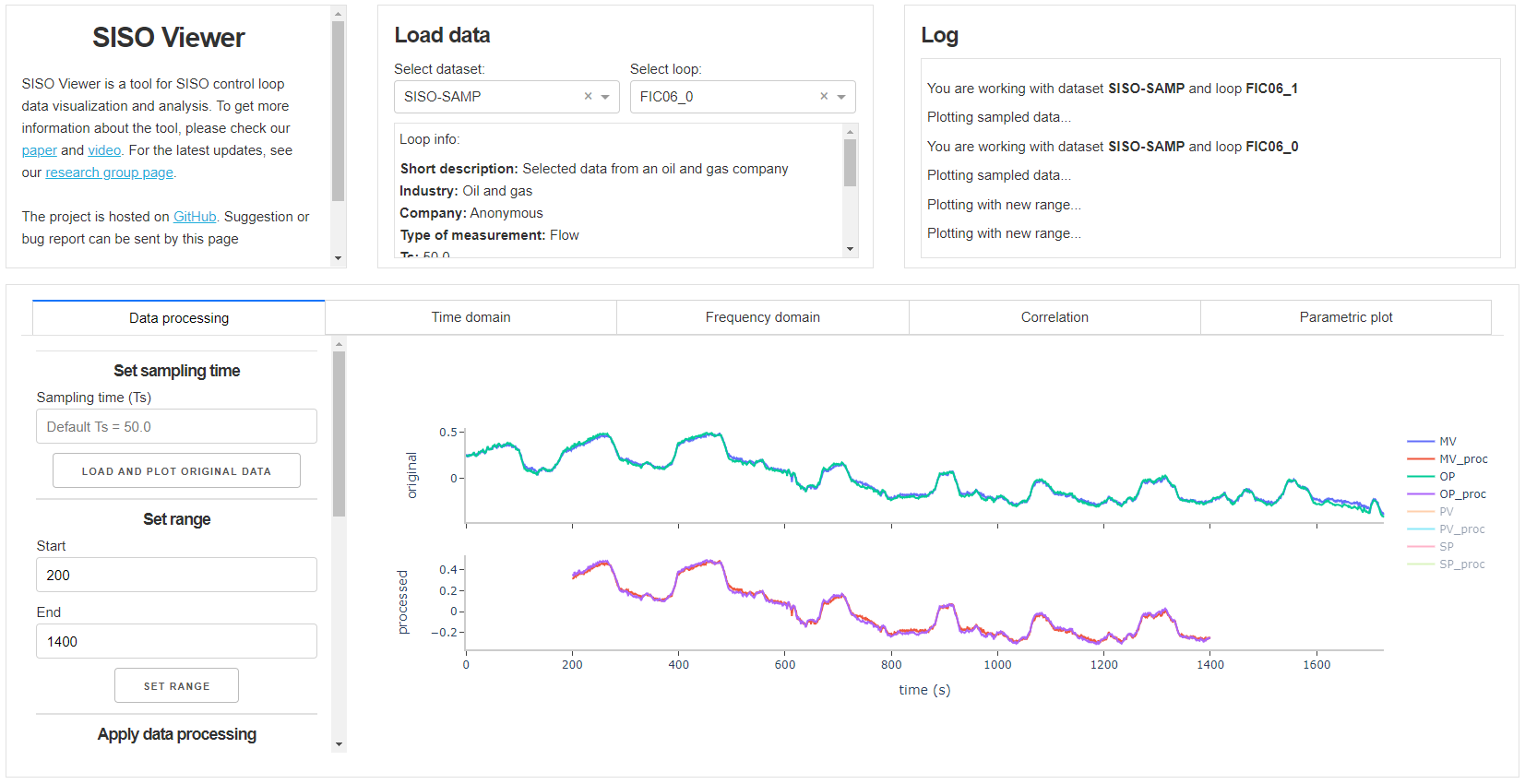
This application aims to facilitate the development and testing of CPM techniques. By using the application, researchers can verify techniques weak points and work on improvements. The application was entirely coded in Python and was designed based on the experience of the authors on CPM techniques development.
More information on https://www.ufrgs.br/gimscop/repository/sisoviewer/
If you used this app in your work, please cite:
DAMBROS, Jônathan WV; TRIERWEILER, Jorge O.; FARENZENA, Marcelo. INDUSTRIAL DATASETS AND A TOOL FOR SISO DATA VISUALIZATION AND ANALYSIS. Computers & Chemical Engineering, p. 107198, 2020.
The portable version includes all that is necessary to run the application (Python, libraries, and data). To run the portable version:
- Download and extract the 7zip file.
- Run the run_app.bat file.
- Wait until the server is set up and paste
http://localhost:8050/to your browser.
Python 3.7 or superior.
Download and extract GitHub repository or clone from GitHub page.
Open Command Prompt (Windows users) or Terminal (Linux and macOS users), navigate to the project folder and run
pip install -r requirements.txt
Make sure Python is in Windows Path (solution).
We recommend working with Virtual Environments.
In the project folder, run
python app.py
Wait until the server is set up and paste http://localhost:8050/ to your browser.
The datasets can be downloaded from the following link.
Extract the datasets from the downloaded file and move the HDF5 files into the data folder in the project root. The application will recognize these files automatically after rerunning.
This is a well-know dataset on CPM. To download the dataset, go to the Jelali's book page. To convert the dataset to HDF5 format, move the .mat file to the data/data_conversion/jelali_huang_to_csv folder.
If using the portable version, run the run_jelali_conversion.bat file in the project root. If not, run (from the project root)
python data\data_conversion\jelali_huang_to_csv\mat_to_csv.py
python data\data_conversion\run_conversion.py
Finnaly, move the jelali_huang.h5 file from the project root to the data folder.
- Load the data - in the Load data section, select the dataset and the loop.
- Plot and process the data - in the Data processing section, select the sampling time, plot the data, select the range and apply data processing.
- Analyze the data and techniques - in the Time domain, Frequency domain, Correlation, and Parametric plot sections, the processed data can be analyzed and the techniques evaluated. These sections are divided into two subsections. The Add to plot subsection contains functions that add new lines to the chart. the Evaluate from data section contains functions that print outputs.
- Hover the question mark or the parameters name to see their description.
- The charts are interactive. To have more information about the interactions, check plotly documentation.
New functions can easily be added to the application. These functions must follow a standard, so they can be read properly by the application. The best way to follow the standard is by copying and changing one of the default functions, which are located in the modules folder. Functions for data processing, for example, are found on the data_processing.py file.
A function is divided into two sections. The first section contains the function description, parameters descriptions, default values, and types. The second section contains the code that is run by the application. New functions must be copied to the corresponding Python file in the modules folder. For example, a function that adds a new line to the time domain chart must be added to the data/modules/time_domain/add.py file
New datasets can also be added. These must be in the default HDF5 format supported by the application, which are generated from CSV files by running the function csv_to_hdf in the data/data_conversion/csv_to_hdf.py file. Together with the CSV files, an Excel file with the loops information must be provided.
To write the default CSV and Excel files, check the Jelali's dataset example in folder data/data_conversion/jelali_huang_to_csv/jelali_huang after running the
python data\data_conversion\jelali_huang_to_csv\mat_to_csv.py mentioned above.
To convert an HDF5 file into CSV files follow the example on data/data_conversion\run_ceonversion.py.
[1] JELALI, Mohieddine; HUANG, Biao (Ed.). Detection and diagnosis of stiction in control loops: state of the art and advanced methods. Springer Science & Business Media, 2009.