This is a project that uses Deep Q-Networks to train an agent to capture yellow bananas and avoid blue bananas through deep reinforcement learning in a Unity ML-Agents environment.
The steps below will describe how to get this running on MacOS:
$ git clone https://github.com/aweeraman/deep-q-networks-navigation.git
Using the Anaconda distribution, create a new python runtime and install the required dependencies:
$ conda create -n dqn python=3.6
$ source activate dqn
$ pip install -r requirements.txt
Download a pre-built environment to run the agent. You will not need to install Unity for this. The environment is OS specific, so the correct version for the operating system must be downloaded.
For MacOS, use this link
After uncompressing, there should be a directory called "Banana.app" in the root directory of the repository.
To run the pre-trained agent, execute the following:
$ python bananas.py --run
To customize hyperparameters and train the agent, execute the following:
$ python bananas.py --train
The state space has 37 dimensions and consists of:
- the agent's velocity
- objects in the agents forward field of view
The agent receives a reward of +1 for a yellow banana, and -1 for blue banana. The goal is therefore to maximize the collection of yellow bananas while minimizing / avoiding blue ones.
The action space for the agent consists of the following four possible actions:
- 0 - walk forward
- 1 - walk backward
- 2 - turn left
- 3 - turn right
The agent must collect a reward of +13 or more in over 100 consecutive episodes to solve the problem.
Q-Learning is an approach which generates a Q-table that is used by an agent to determine best action for a given state. This technique becomes difficult and inefficient in environments that have a large state space. Deep Q-Networks on the other hand makes use of a neural network to approximate Q-values for each action based on the input state.
However, there are drawbacks in Deep Q-Learning. A common issue is that the reinforcement learning tends to be unstable or divergent when a non-linear function approximator such as neural networks are used to represent Q. This instability comes from the correlations present in the sequence of observations, the fact that small updates to Q may significantly change the policy and the data distribution, and the correlations between Q and the target values. [1]
To overcome this, experience replay is a technique that was used in this solution that uses the biologically inspired approach of replaying a random sample of prior actions to remove correlations in the observation sequence and smooth changes in the data distribution.
- Fully connected layer 1: Input 37 (state space), Output 32, RELU activation
- Fully connected layer 2: Input 32, Output 32, RELU activation
- Fully connected layer 3: Input 32, Output 4 (action space)
The hyperparameters for tweaking and optimizing the learning algorithm were:
- max_t (750): maximum number of timesteps per episode
- eps_start (1.0): starting value of epsilon, for epsilon-greedy action selection
- eps_end (0.01): minimum value of epsilon
- eps_decay (0.9): multiplacative factor (per episode) for decreasing epsilon
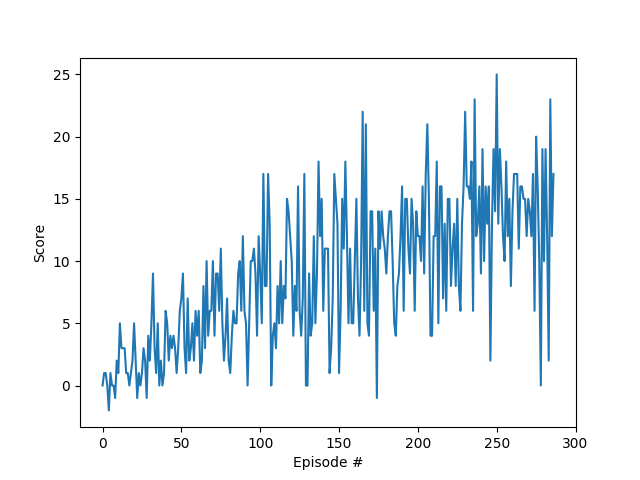
Below is a training run of the above model architecture and hyperparameters:
Number of agents: 1
Number of actions: 4
Episode 100 Average Score: 3.97
Episode 200 Average Score: 9.51
Episode 287 Average Score: 13.12
Environment solved in 187 episodes! Average Score: 13.12
The plot of rewards for this run is as follows:
Further optimization of this architecture can be performed by training with different hyperparameters to get faster and better learning outcomes. A couple of further approaches to try out are:
- Double Q-Learning
- Delayed Q-Learning
If you run into an error such as the following when training the agent:
ImportError: Python is not installed as a framework. The Mac OS X backend will not be able to function correctly if Python is not installed as a framework. See the Python documentation for more information on installing Python as a framework on Mac OS X. Please either reinstall Python as a framework, or try one of the other backends. If you are using (Ana)Conda please install python.app and replace the use of 'python' with 'pythonw'. See 'Working with Matplotlib on OSX' in the Matplotlib FAQ for more information.
Modify ~/.matplotlib/matplotlibrc and add the following line:
backend: TkAgg
1 - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Q-learning#Deep_Q-learning