- Presentation model 將 state 跟 behavior 從 view class 抽離出來成為 (self-contained) model calss,也就是 presentation 拆成 view class 與 model class,而 view 只是將 model 的 state 映射 (project) 到 UI 上而已。
- 所謂 self-contained 是因為 presentation model 自己維護一份 (dynamic) state,不需要向 view class 取用 state。由於跟 GUI framework 無關,所以方便測試,但要多寫 synchronization code 來同步 view 與 presentation model 兩邊的 state。
- Presentation model 背後會協調 domain layer (裡的多個 domain object),並向外提供一個 interface,才不用在 view class 裡做 decision making。要注意 presentation model 並不是是通往 domain layer 的 GUI-friendly facade,而是跟 GUI framework 無關的抽象層 (abstract of the view)。
參考資料:
-
-
Represent the STATE AND BEHAVIOR OF THE PRESENTATION independently of the GUI controls used in the interface.
把 presentation 的 state & behavior 從 GUI control (也就是 widget 及 view class) 層抽離出來。
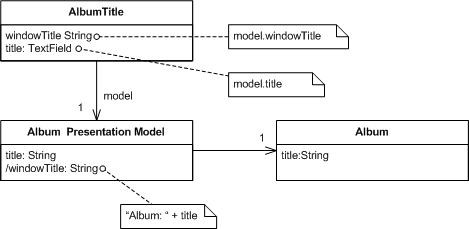
GUI control (AlbumTitle) 相依於 presentation model (Album Presentation Model),而 presentation model 背後則是由 domain model (Album) 支撐;在 GUI control 裡,就是用
model.xxx的方式跟 presentation model 同步 state (像 .NET 的 data binding 可以減少手動同步的工) -
GUIs consist of widgets that contain the STATE OF THE GUI SCREEN. Leaving the state of the GUI in widgets makes it harder to get at this state, since that involves manipulating widget APIs, and also encourages putting PRESENTATION BEHAVIOR in the view class.
GUI 由內含 state 的 widget 組成,若將 state 留在 widget 裡,就得要透過 widget API 才能取得,也因此很容易將 presentation behavior/logic 放進 view class 裡。
注意這裡 "state of the GUI screen" 及 "state and behavior of the presentation" 的差別,前者講的是 GUI/view,後者是稍微抽象一點且跟 GUI Framework 無關的 presentation。其中 "presentation behavior" 換成 "presentation logic" 會比較好懂,就是 UML 裡的
windowTitle = "Album: " + title,若不是抽出 presentation model,這段邏輯就會在留在 view class 裡。 -
Presentation Model PULLS the STATE AND BEHAVIOR OF THE VIEW out into a model class that is PART OF THE PRESENTATION. The Presentation Model COORDINATES with the DOMAIN LAYER and provides an interface to the view that MINIMIZES DECISION MAKING IN THE VIEW.
重點就在 decision making in the view,也就是 UML 圖中的
windowTitle = "Album: " + title(behavior/logic),放在 view 裡會很難測,因為相依於 GUI Framework。The view either stores all its state in the Presentation Model or synchronizes its state with Presentation Model frequently
只是 2 種不同的說法 -- view 的 state 源自 presentation model,view 也不會留存一份 (否則會失去同步)
-
Presentation Model may interact with several domain objects, but Presentation Model is not a GUI friendly facade to a specific domain object. Instead it is easier to consider Presentation Model as an ABSTRACT OF THE VIEW THAT IS NOT DEPENDENT ON A SPECIFIC GUI FRAMEWORK.
While several views can utilize the same Presentation Model, each view should require only one Presentation Model. In the case of composition a Presentation Model may contain one or many CHILD Presentation Model instances, but each CHILD CONTROL will also have only one Presentation Model.
每個 view class 只能對應一個 presentation model (雖然多個 view 可能共用一個 presentation model);一個複雜的頁面 (composition) 可能 presentation model 由多個 child presentation model 組成,不過每個 child control 還是只對應一個 presentation model -- 可以跟 parent control 共用同一個 presentation model。
-
Presentation model 將 state 跟 behavior 從 view class 抽離出來成為 (self-contained) model calss,也就是 presentation 由 view class 與 model class 共同組成,而 view 只是將 model 的 state 映射 (project) 到 UI 上而已。
-
Presentation model 背後會協調 domain layer (裡的多個 domain object),並向外提供一個 interface,減少在 view class 裡做 decision making。別把 presentation model 當做是通往 domain layer 的 GUI-friendly facade,而是跟 GUI framework 無關的抽象層 (abstract of the view),
-
Presentation model 有 view 上所有 dynamic information 的 data fields,不只是 content,還包括像 enablement state (enabled/disabled);以 Figure 1 為例,雖然 composer filed 的 enablement 由
isClassical來決定,但在 presentation model 上還是會有個shouldEnableComposer把return isClassical的邏輯封裝起來,除了讓 view 儘量保持單純 (這跟 passive view 裡 dumb view 的說法有點像),也明確指出 decision making 是 presentation model 的責任。 -
Figure 2 是個 running example,當使用者按下 classical (checkbox) 時,view 的 event handler 會將 view state 寫到 presentation model (
pmod.isClassical = view.classical.checked),然後根據 presentation model 更新 composer (field) 的 enablement (view.composerField.enabled = pmod.isComposerEnabled)。當使用者按下 apply 時,view 會轉換叫pmod.apply(),更新 domain layer (album.isClassical = presentationModel.isClassical)。 -
採用 presentation model 最惱人的是 view 跟 presentation model 間的同步 (synchronization),該把 synchronization code 放 view 還是 model? 也就是參照的方向是 view -> model 或 model -> view? 雖然 sychronization code 有可能出錯,但也容易找到跟修復,若想將 synchronization code 也納入測試的話,則建議採用 model -> view 的做法,因為測試 presentation model 時也測得到,相對於涉及 GUI framework 的 view 也比較好測。
-
Model -> view 的做法會讓 view 變得更加無腦 (dumb) - 提供 setters 讓 model 更新 state,同時也觸發事件 (轉通知 presentation model) 以回應使用者的操作,通常 view 會實作某個 interface,所以在測試 presentation model 時方便做 stubbing;這不正是 Passive View 的做法?
-
Presentation model 跟 Supervising Controller 及 Passive View 要解決的問題類似 - 測試時不需要 UI,但 presentation model 更強調獨立於 view (聽起來 view -> model 的做法是 Presentation Model 比較正統的做法?),不需要 view 提供 state,也因此要有 synchronization code 處理兩邊 state 的同步,這是 Passive View 不需要的。
-
- 感覺 Passive View 像是 Presentation Model 的一種,尤其是 presentation model 持有 view 參照的這種做法。
- 但根據 Presentation Model When to Use It 的說法,跟 Passive View 在解決類似的問題 (test without the UI) 而已。
參考資料:
- Presentation Model https://martinfowler.com/eaaDev/PresentationModel.html
- "A Presentation Model that references a view ..." 這個段落提到 "The resulting view is very dumb",在加上 "The view contains setters for any state that is dynamic and raises events in response to user actions",幾乎就是 passive view 裡 dumb view 的說法
- 在 When to Use It 提到 Presentation Model 跟 Passive View 都在解決 "test without the UI" 的問題,只是 Passive View 不需要處理 model 與 view 間的 synchronization? 在想應該是因為 presenter 沒有持有一份 state 的關係...
- View class 持有 presentation model 的 reference,由 view class 主動根據 model 的 state 更新 UI;雖然 presentation model 可以被多個 view 共用,但一個 view 只能對應一個 presentation model。
- 由於 view -> model 的關係,而且 model 也不應該知道 view,所以 synchronization code 會寫在 view class 裡 (
model.xxx),雖然要藉由 view class 的測試才測得到 (涉及 GUI framework,比較難測)。 - Presentation model 有 view 上所有 dynamic information 的 data fields,不只是 content,還包括像 enablement state (enabled/disabled)。例如管理者才能重啟系統,雖然 view 也可以根據
model.isAdmin決定restartButton.enabled,但還是要用另一個model.allowedToRestart來將return isAdmin的邏輯封裝起來 (或許由 domain layer 來決定會更好,例如system.allowedToRestart(currentUser)),也明確指出 decision making 是 presentation model 的責任。
參考資料:
- Presentation Model https://martinfowler.com/eaaDev/PresentationModel.html
- Presentation Model https://martinfowler.com/eaaDev/PresentationModel.html
- 提到 "consider Presentation Model as an abstract of the view that is not dependent on a specific GUI framework",但像 Flask + WTForm 的組合,presentation model 因為 form 的關係,如何跟 UI framework 拆離?
- 不過 "In the case of composition a Presentation Model may contain one or many child Presentation Model instances, but each child control will also have only one Presentation Model." 好像提供了答案? 畫面上的表單對應
model.form.xxx...